At its two sites in Hauts-de-France and Bordeaux, ELISA Aerospace favors small classes and small groups for practical work and language courses, enabling each student to benefit from permanent supervision and ensuring close contact between student engineer and teacher.

The teaching provided at ELISA Aerospace combines traditional practices for transmitting knowledge and know-how with other methods supported by Information and Communication Technologies for Teaching (ICTT).
In particular, the use of graphic tablets for teachers enables lively and effective remote interaction with students, whatever the circumstances. This dynamic is underpinned by a Digital Workspace used daily by students and teachers.
ELISA Aerospace’s teaching system is based on theEuropean Credit Transfer System(ECTS), which facilitates the international opening of the training provided by ELISA Aerospace (European LMD model). This system applies to all ELISA Aerospace training courses as part of the assessment of knowledge or skills.
ECTS credits are an assessment given to Teaching Units (UE) to evaluate the workload required of students to obtain them. They reflect the amount of work required for each ECUE in relation to the total amount of work needed to complete the year’s studies.
To validate a year and be allowed to move on to the next year, a student must acquire 60 ECTS credits, divided equally between the two semesters of the year (30 and 30). These credits are obtained if and only if the engineering student passes his/her exams.
ELISA Aerospace has set up individualized pathways to ensure that the diversity of students’ backgrounds is taken into account when they enter the preparatory cycle.
With the new bac, profiles are diversified, and so are the ways in which skills are acquired. The first few weeks of ELISA 1 are dedicated to bringing students up to speed in core subjects.
ELISA Aerospace fine-tunes its systems in response to the health situation and the constraints imposed on the final-year students.
ELISA Aerospace’s two campuses are equipped with a range of pedagogical tools to provide its engineering students with the best possible training right from the integrated preparatory cycle (non-exhaustive list):
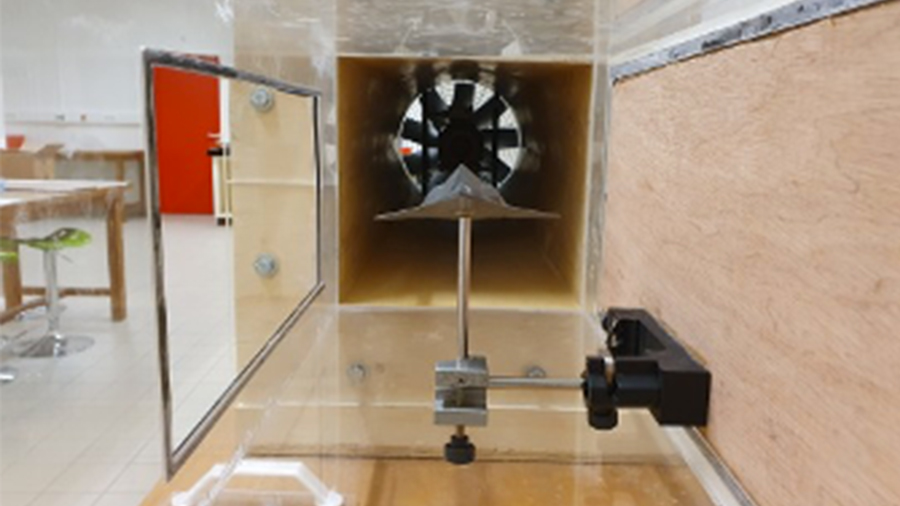
As part of a partnership with ISAE-ENSMA, engineering students at ELISA Aerospace Hauts-de-France have just completed the construction of a subsonic wind tunnel made entirely of wood and fitted with a Plexiglas experimental section.
For educational purposes, it can be used to visualize air flows around a wing or aircraft profile, and to measure lift and drag on models produced by additive manufacturing on the school’s premises.
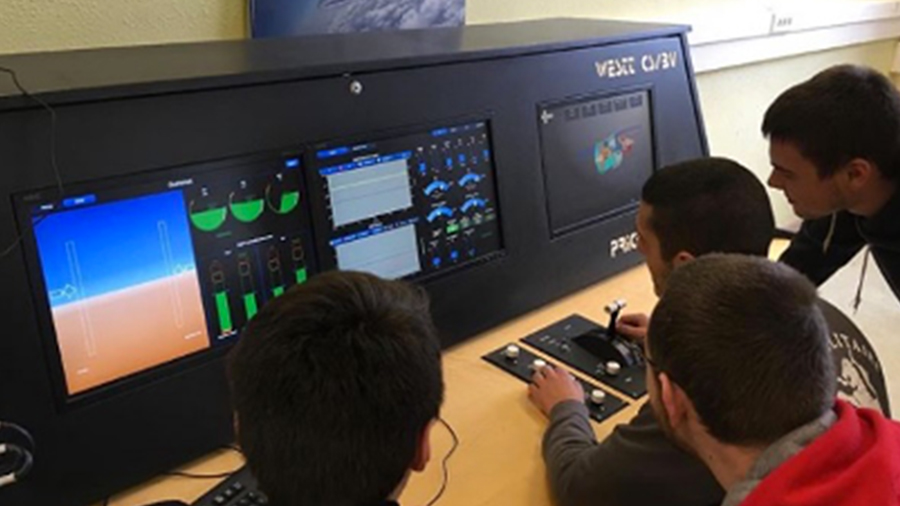
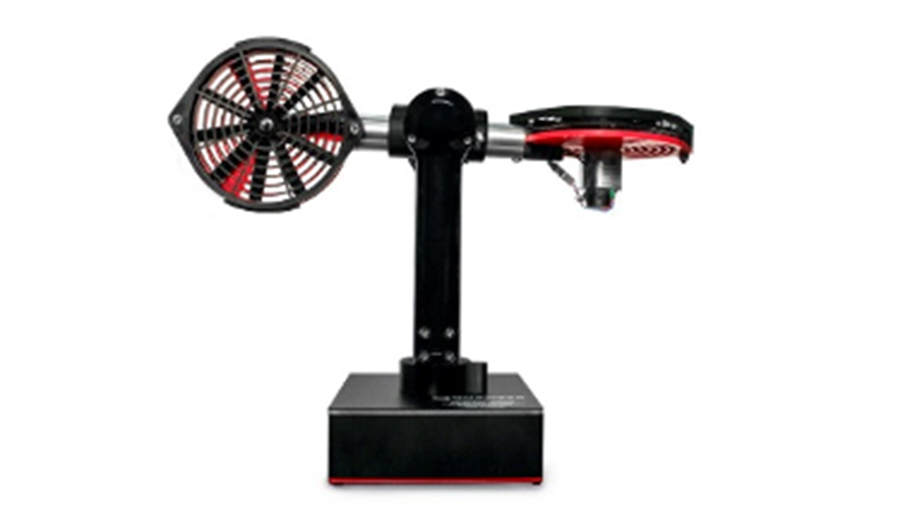


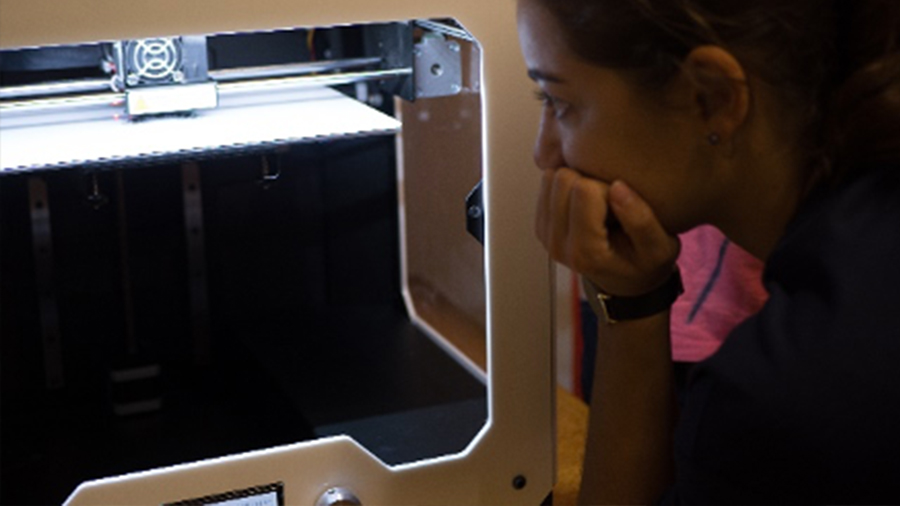

A range of Quanser educational models is currently being developed to provide a set of complex physical systems for applying the concepts of modeling and control developed throughout the engineering cycle during practical work sessions.













114 allée des charbonnières
33127 Saint Jean d'Illac
06 48 95 76 72
contactbdx@elisa-aerospace.fr
48 rue Raspail
02100 Saint-Quentin
03 23 68 06 11
contact@elisa-aerospace.fr